Sun Protection Beyond SPF: New Ways to Guard Your Skin. SPF alone isn’t enough. This deep dive reveals the limitations of sun protection factor, exploring the crucial role of shade, clothing, skincare routines, and lifestyle choices. Discover how to maximize your sun protection game, from understanding UVA and UVB rays to choosing the right clothing and products, and beyond. Get ready to level up your skin-saving strategies!
We’ll unpack the science behind sun damage, highlighting how SPF alone falls short. Learn about the hidden dangers of UVA rays, and how to combat them effectively. From strategic shade-seeking to the right clothing choices, we’ll provide practical tips to optimize your sun protection routine. Prepare to discover a holistic approach to sun safety, covering everything from skincare to lifestyle adjustments.
Understanding the Limitations of SPF
Sunscreen, with its SPF rating, is a crucial part of our sun protection routine. But understanding *how* SPF works, and its inherent limitations, is key to truly safeguarding your skin. It’s not just about slapping on some lotion and forgetting about it—there’s a lot more to sun protection than meets the eye.
SPF, or Sun Protection Factor, essentially measures how much longer you can stay in the sun before your skin starts to burn compared to when you’re not wearing sunscreen. A higher SPF number translates to longer protection, but it doesn’t mean complete immunity from sun damage.
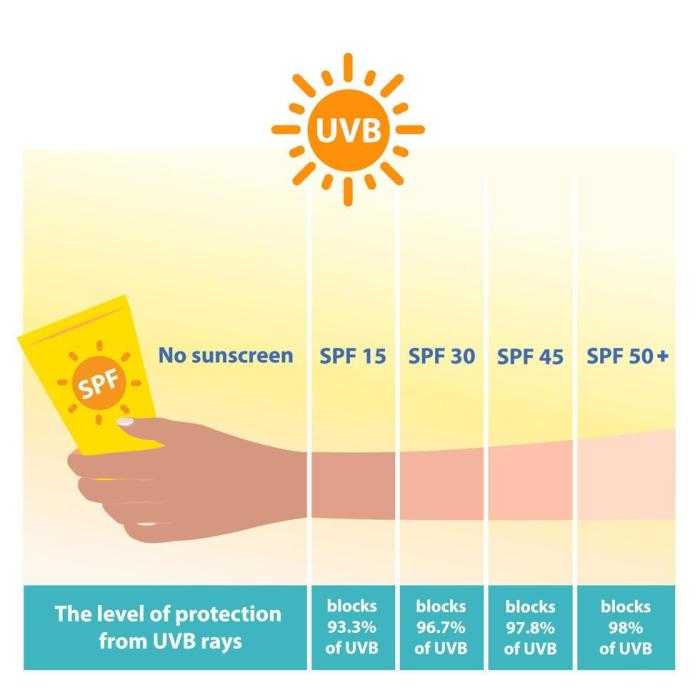
How SPF Ratings Work
SPF ratings are calculated by measuring the amount of UVB radiation it takes to cause redness in skin with and without sunscreen. The number represents the ratio of time you can stay in the sun with sunscreen compared to the time it takes for your skin to burn without it. For example, SPF 30 means you can stay 30 times longer in the sun before experiencing sunburn. This is a crucial factor to consider, but it doesn’t account for UVA rays.
UVA vs. UVB Rays
The sun emits two types of ultraviolet (UV) rays: UVA and UVB. While UVB rays are primarily responsible for sunburn, UVA rays penetrate deeper into the skin, causing long-term damage like premature aging, wrinkles, and an increased risk of skin cancer. Crucially, SPF ratings primarily focus on UVB protection, leaving a significant gap in UVA defense.
Limitations of SPF Protection
SPF protection isn’t foolproof. Several factors can reduce its effectiveness:
- Sweating and Swimming: Sunscreen can be washed away or diluted by sweat and water, significantly reducing its protective effect. Regular reapplication is essential, especially after swimming or sweating heavily.
- Reapplication: Sunscreen needs to be reapplied frequently, typically every two hours or after swimming or sweating. Failure to do so compromises the protection provided by the sunscreen. A common misconception is that applying a thicker layer of sunscreen will increase the protection, but this is not the case. A proper amount of sunscreen should be applied to the skin for optimal protection.
- Inadequate Product Application: Applying an insufficient amount of sunscreen can lead to a lower effective SPF. The general recommendation is to use about a shot glass’s worth of sunscreen for an average adult’s body. Proper application ensures uniform coverage, crucial for effective protection.
UVA Damage: A Deeper Look
UVA rays penetrate deeply into the skin, damaging collagen and elastin fibers. This gradual damage leads to premature aging, wrinkles, and an increased risk of skin cancer. The effects of UVA damage are often subtle and develop over time, unlike the immediate, visible effects of UVB burns. It’s a slow, insidious process that can have significant long-term consequences.
Examples of Inadequate SPF Protection
While a high SPF rating is beneficial, it’s crucial to understand that the protection might not always align with the SPF number listed on the label. Some products may not provide adequate UVA protection, even if they have a high SPF rating for UVB. In such cases, choosing a sunscreen specifically formulated with broad-spectrum protection (protecting both UVA and UVB rays) is crucial. There are many examples of products that fall short of providing adequate sun protection beyond the stated SPF rating. It’s always best to check the product label for specific UVA protection claims, as these are often less visible than the UVB SPF rating.
Beyond SPF
Sunscreen, with its SPF rating, is a crucial part of sun protection, but it’s not the whole story. Think of SPF as a vital tool in your sun safety arsenal, but it needs support from other strategies. Effective sun protection goes beyond slathering on sunscreen; it’s a holistic approach that considers various factors to shield your skin from the sun’s harmful rays.
Protecting your skin from the sun’s damaging ultraviolet (UV) rays is a multifaceted endeavor. Simply applying sunscreen, while essential, isn’t enough. Complementary strategies like seeking shade, wearing protective clothing, and understanding the limitations of sunscreen usage are equally important. This proactive approach minimizes your skin’s exposure to UV rays, thereby reducing your risk of sunburn, premature aging, and skin cancer.
Protective Strategies
Various methods complement sunscreen, creating a comprehensive approach to sun safety. These strategies work synergistically to minimize your skin’s exposure to harmful UV rays. By combining multiple strategies, you significantly enhance your overall sun protection.
Seeking Shade
Protecting your skin from the sun’s intense rays is crucial, particularly during peak sun hours. The sun’s rays are strongest between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., so it’s vital to seek shade during these periods. This significantly reduces your skin’s exposure to UV radiation, minimizing your risk of sunburn and long-term skin damage. Finding shaded areas, like trees, canopies, or buildings, is a practical way to limit direct sun exposure.
Clothing as a Sun Barrier
Clothing acts as a physical barrier, shielding your skin from the sun’s harmful UV rays. Different fabrics and types of clothing offer varying levels of protection. Wearing appropriate clothing is an important part of a comprehensive sun protection strategy.
Types of Protective Clothing
Various clothing items offer varying levels of sun protection. Wide-brimmed hats provide shade for your face, ears, and neck, reducing direct sun exposure on these sensitive areas. Long-sleeved shirts and pants cover larger portions of your skin, providing more comprehensive protection. Protective clothing options include:
- Wide-brimmed hats:
- Long-sleeved shirts and pants:
- Sunscreen clothing (specifically designed for sun protection):
- Lightweight fabrics like linen or cotton:
Choosing Protective Clothing, Sun Protection Beyond SPF: New Ways to Guard Your Skin
When selecting clothing for sun protection, consider the fabric’s weave and the material’s properties. Look for clothing with a tight weave that blocks UV rays more effectively. The color of the clothing also matters, as darker colors may absorb more UV radiation than lighter ones.
Comparing Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of Clothing
The sun protection factor (SPF) of clothing varies depending on the fabric and its weave. A higher SPF indicates greater protection against UV rays.
| Clothing Type | Approximate SPF |
|---|---|
| Loose-weave cotton | 2-4 |
| Dense-weave cotton | 5-8 |
| Lightweight linen | 5-7 |
| Moisture-wicking synthetic fabrics | 7-15 |
| Specialized sunscreen clothing | 30-50+ |
Skin-Care Routines for Sun Protection
Source: vecteezy.com
Protecting your skin from the sun goes way beyond just SPF. Think about layering up your wardrobe with essentials—like a good, wide-brimmed hat, or those long-sleeved shirts you always seem to forget about. Investing in quality basics like these, as discussed in The Unsung Heroes of Your Wardrobe: The Power of Perfect Basics , is key for shielding your skin from harmful rays.
After all, a stylish and practical wardrobe is a fantastic part of a sun-smart routine!
Sunscreen is just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to shielding your skin from the sun’s harmful rays. Beyond the SPF number, a comprehensive skincare routine plays a crucial role in daily sun protection. This routine isn’t just about applying sunscreen; it’s about creating a layered defense against the sun’s damaging effects. Let’s dive deeper into the skincare strategies that go beyond the basics.
Skincare products, especially those formulated with sun protection in mind, significantly enhance your defense against the sun. They act as a shield, preventing UV rays from penetrating the skin and causing damage. Think of it like a multi-layered fortress, with each product adding to the overall protection.
The Crucial Role of Broad-Spectrum Sunscreens
Broad-spectrum sunscreens are essential for comprehensive sun protection. They protect against both UVA and UVB rays, which are both harmful to the skin. UVA rays penetrate deeper, contributing to premature aging and long-term damage, while UVB rays cause sunburn and other immediate skin issues. Choosing a broad-spectrum sunscreen is paramount for effective protection.
Ingredients for Enhanced Sun Protection
Beyond the SPF, certain ingredients in skincare products offer additional sun protection. Antioxidants, like vitamin C and E, help neutralize free radicals produced by UV exposure, mitigating cellular damage. Plant extracts, such as aloe vera and green tea, have soothing and protective properties. Incorporating these ingredients into your routine can significantly enhance your skin’s defenses.
Daily Sunscreen Application, Even on Cloudy Days
Don’t underestimate the sun’s power on cloudy days. Clouds do filter some UV radiation, but a significant portion still reaches the Earth’s surface. Daily application of sunscreen, even when the sun isn’t directly shining, is vital for consistent protection. This habit forms a protective shield, safeguarding your skin throughout the day.
Skin Type Considerations
Different skin types react differently to various sun protection products. Oily skin might benefit from lightweight, oil-free sunscreens, while dry skin might require a richer, moisturizing formula. Understanding your skin’s specific needs helps you choose the right products for optimal protection and comfort.
Daily Skincare Routine for Sun Protection
| Step | Product | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Morning Cleansing | Gentle cleanser | Remove overnight impurities and prepare skin for sun protection. |
| 2. Moisturizer | Moisturizer with SPF | Hydrate skin while providing a layer of sun protection. |
| 3. Targeted Treatment (optional) | Spot treatment (e.g., acne) | Apply as needed, after moisturizer. |
| 4. Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen | High SPF sunscreen | Apply liberally 15-30 minutes before sun exposure. Reapply every two hours or immediately after swimming or sweating. |
| 5. Evening Cleansing | Gentle cleanser | Remove accumulated dirt and makeup. |
| 6. Night Moisturizer | Moisturizer suitable for nighttime use | Nourish skin while it repairs itself overnight. |
Lifestyle Factors for Sun Protection: Sun Protection Beyond SPF: New Ways To Guard Your Skin
Beyond sunscreen, your everyday choices significantly impact your skin’s resilience against the sun’s harmful rays. Healthy habits, from hydration to nutrition, play a crucial role in building a sun-safe lifestyle. Adopting these practices is not just about avoiding sunburn; it’s about preserving your skin’s youthful glow and overall well-being.
Lifestyle choices, when combined with consistent sun protection measures like sunscreen, create a powerful shield against sun damage. This comprehensive approach ensures your skin remains healthy and vibrant, fighting off premature aging and other potential issues.
Hydration and Skin Health
Adequate hydration is essential for maintaining healthy skin. Water is the lifeblood of your body, and your skin is no exception. Proper hydration helps to keep your skin plump and supple, making it more resilient to environmental stressors, including the sun. Dehydrated skin is thinner and more prone to damage, increasing its vulnerability to sun-induced damage. The importance of hydration is undeniable, so maintaining a consistent intake of water throughout the day is a vital step towards healthy skin.
Sun Exposure and Skin Aging
Prolonged and unprotected sun exposure is a major contributor to premature skin aging. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun triggers the formation of free radicals, which damage collagen and elastin fibers, leading to wrinkles, age spots, and sagging skin. Sun damage can accumulate over time, leading to visible signs of aging even in relatively young individuals. Protecting your skin from the sun’s rays is critical in preserving its youthful appearance and reducing the long-term effects of sun exposure.
Nutrition and Healthy Skin
A balanced diet rich in antioxidants and essential nutrients is crucial for supporting healthy skin and bolstering its natural defenses against sun damage. Nutrients like vitamin C, vitamin E, and beta-carotene play a vital role in neutralizing free radicals and protecting skin cells from damage. Consuming foods rich in these nutrients can significantly improve your skin’s ability to withstand sun exposure. Healthy dietary choices contribute to overall skin health, improving its resilience against environmental aggressors.
Healthy Foods for Skin Protection
Numerous foods offer valuable nutrients for skin protection. Leafy green vegetables, rich in antioxidants, are excellent choices. Berries, packed with vitamin C, are also beneficial. Fatty fish, a source of omega-3 fatty acids, help maintain skin hydration and elasticity. These are just a few examples of the many nutritious foods that contribute to skin health and resilience against sun damage.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens are excellent sources of vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A, C, and K, which contribute to overall skin health. They are also rich in antioxidants, helping protect skin cells from damage caused by free radicals.
- Berries: Strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries are abundant in vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant that protects against free radical damage and helps maintain collagen production.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, tuna, and mackerel are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids, which contribute to skin hydration and elasticity. These essential fats help maintain the skin’s moisture barrier, reducing its susceptibility to dryness and damage.
- Citrus Fruits: Oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are high in vitamin C, which supports collagen production and protects against free radical damage.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and chia seeds are rich in vitamin E, a powerful antioxidant that helps protect skin cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Lifestyle Choices and Sun Protection Impact
| Lifestyle Choice | Impact on Sun Protection |
|---|---|
| Hydration | Maintains skin hydration, improving resilience to sun damage. |
| Sun Exposure Management | Reduces direct sun exposure, minimizing skin damage. |
| Balanced Diet | Provides essential nutrients for skin health, enhancing its ability to withstand sun damage. |
| Regular Exercise | Improves circulation and skin’s ability to repair damage. |
| Stress Management | Reduces oxidative stress, improving skin’s ability to repair damage. |
Sun Protection for Different Demographics
Protecting your skin from the sun’s harmful rays isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach. Different demographics have varying sensitivities and needs, demanding tailored sun protection strategies. Understanding these differences is crucial for ensuring everyone can enjoy the outdoors while minimizing their skin cancer risk. From the delicate skin of children to the unique concerns of older adults, this section delves into the specifics of sun protection for diverse groups.
Different factors influence the skin’s susceptibility to sun damage, including genetics, pre-existing medical conditions, and lifestyle choices. Age plays a significant role, as the skin’s ability to repair itself diminishes with time. This necessitates tailored sun protection strategies for various demographics. Let’s explore the unique sun protection needs of different groups.
Sun Protection for Children
Children’s skin is particularly vulnerable to sun damage due to its thinner epidermis and higher sensitivity. Prolonged exposure can lead to sunburn, premature aging, and increase the risk of skin cancer later in life. Prioritizing sun protection in childhood is vital for long-term skin health.
- Sunscreen application is crucial: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to all exposed skin areas, including the face, ears, and backs of the knees. Reapply frequently, especially after swimming or sweating.
- Protective clothing is essential: Utilize clothing with UPF (Ultraviolet Protection Factor) ratings to shield the skin from direct sunlight. Wide-brimmed hats and sunglasses are also important.
- Seek shade during peak sun hours: Limit outdoor activities during the midday hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.) when the sun’s rays are strongest. Finding shady spots under trees or using umbrellas can offer crucial protection.
Sun Protection for Older Adults
Older adults often experience reduced skin elasticity and decreased melanin production, making them more susceptible to sun damage and skin aging. Skin cancer risk also increases with age.
- Increased sunscreen use: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher liberally and frequently to all exposed skin areas. Reapply every two hours or immediately after swimming or sweating.
- Emphasis on protective clothing: Wearing protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts and pants, is crucial. Wide-brimmed hats and sunglasses are essential accessories for complete protection.
- Regular skin checks: Regular self-exams for skin changes are essential for early detection of skin cancer. Consult a dermatologist for regular check-ups.
Sun Protection for Individuals with Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can increase sensitivity to sunlight. For example, individuals with photodermatoses or those taking certain medications may require enhanced sun protection.
- Consult a healthcare professional: It’s vital to consult a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate sun protection measures for specific medical conditions. They can provide personalized recommendations based on the individual’s condition.
- Higher SPF and protective clothing: Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF (at least 50) and consider protective clothing, especially for prolonged sun exposure.
- Strict adherence to guidelines: Follow the prescribed guidelines for sunscreen application and reapplication, and seek shade during peak sun hours.
Comparing Sun Protection Needs Across Age Groups
| Age Group | Sun Protection Needs | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| Children (0-12) | High sensitivity to sun damage, thinner epidermis. | High SPF sunscreen, protective clothing, shade, frequent reapplication. |
| Adults (13-64) | Maintain healthy skin habits for long-term protection. | Broad-spectrum sunscreen, protective clothing, shade, reapplication. |
| Older Adults (65+) | Reduced skin elasticity, decreased melanin production. | High SPF sunscreen, protective clothing, shade, regular skin checks. |
Illustrative Examples of Sun Protection Strategies
Source: vectorstock.com
So, you’ve learned about SPF limitations and the importance of a holistic approach to sun protection. Now, let’s dive into practical examples. We’ll explore how everyday people are incorporating sun protection into their routines, demonstrating the effectiveness of combining various strategies for maximum shield against the sun’s harmful rays.
Understanding how to weave sun protection into your daily life is key to long-term skin health. This section illustrates practical examples of incorporating sun protection measures, highlighting the value of proactive strategies rather than just reactive ones.
A Day in the Life of Maya: Sun Protection in Action
Maya, a busy graphic designer, understands the importance of sun protection. Her daily routine is a testament to proactive sun safety. She recognizes that sun damage isn’t just about beach days; it’s about cumulative exposure throughout the year.
- Morning Routine: Maya starts her day with a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30, applied liberally 15-20 minutes before heading out. She applies it to all exposed skin, including her face, neck, ears, and even the tops of her hands. Imagine a smooth, even layer of protection, like a second skin, shielding her from the sun’s rays.
- Lunch Break: While grabbing lunch, Maya opts for a shaded spot under a tree, reducing direct sun exposure. She carries a reusable water bottle, staying hydrated throughout the day to maintain healthy skin, which is more resilient to the effects of sun damage.
- Outdoor Activities: When working outdoors, Maya utilizes a wide-brimmed hat and sunglasses with UV protection. She uses these simple accessories as a shield against the sun, preventing direct contact with her face and eyes. Visualize a stylish hat casting a shadow over her face, and sunglasses blocking the sun’s glare.
- Evening Skincare: After a long day, Maya diligently cleanses her face and applies a hydrating serum with antioxidant properties. This nighttime routine helps to repair any damage accumulated during the day. Imagine a soothing skincare routine that promotes healthy skin cell renewal.
Combining Strategies for Maximum Protection
Maya’s routine showcases how various strategies can be combined for maximum sun protection. This isn’t just about one single method; it’s about a layered approach.
| Strategy | Description | Visual Representation |
|---|---|---|
| Sunscreen | A broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, applied liberally 15-20 minutes before sun exposure. | Imagine a smooth, even layer of protection over exposed skin. |
| Shade | Seek shade during peak sun hours (10 am to 4 pm) | Visualize a shaded spot under a tree or umbrella. |
| Protective Clothing | Wear protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts and pants, when possible. | Imagine comfortable, long-sleeved clothing that provides a barrier against the sun. |
| Sunglasses | Wear sunglasses with UV protection to shield eyes and sensitive skin around the eyes. | Visualize sunglasses that block harmful UV rays. |
Case Study: A Journey Towards Improved Sun Protection
Aisha, a young woman initially unaware of the long-term effects of sun exposure, embarked on a journey to improve her sun protection habits. Initially, she relied solely on sunscreen. Gradually, she integrated protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses into her routine. This gradual transition demonstrates the importance of consistency and building healthy habits.
Final Summary

Source: verywellhealth.com
So, SPF isn’t the sole savior. This exploration of sun protection beyond the SPF rating unveils a multifaceted approach to safeguarding your skin. From understanding the nuances of UVA and UVB rays to incorporating protective clothing and lifestyle adjustments, this comprehensive guide equips you with the knowledge to conquer the sun’s harmful rays. Remember, sun protection is an ongoing journey, one that requires conscious choices and a proactive approach. Embrace the new, holistic way to protect your skin from the sun’s relentless rays!